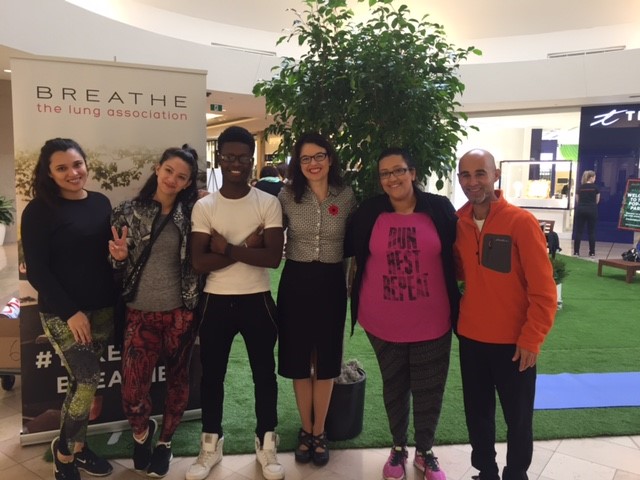On average, everyone takes an astonishing 22,000 breaths per day – something we’re not conscious of doing. And, although breathing is fundamental to life, lung research doesn’t get the attention it truly needs.
November is Lung Month, the perfect time to reinforce and remind Canadians how important it is to #TakeABreather. To capture attention, invite participation and help raise donations for lung research, The Lung Association is launching interactive pop-up parks across Canada.
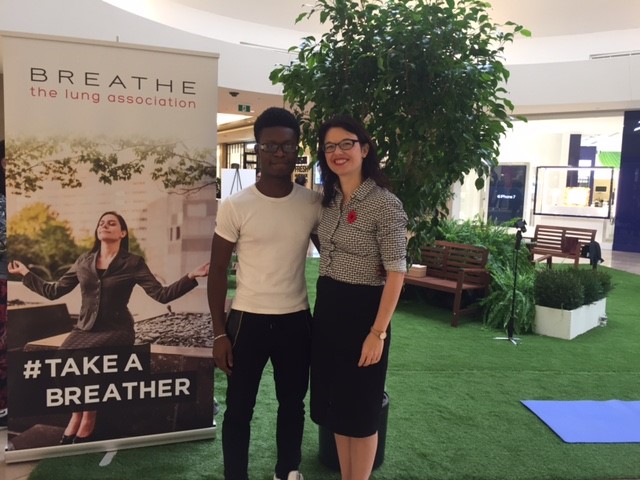

Joseph Neale is a “Breathing Ambassador” who survived lung cancer when he was only 20 years old. Despite having surgery he got his voice back and is hoping to win a “Grammy for Lung Cancer Research”. Together we answered questions at the #TakeABreather pop-up park at Sherway Gardens. Stories like his remind me that I need to be the best scientist that I can be to make the discoveries that will improve the lives of those living with lung disease.
Highlight’s of the kick off were livestreamed on Breathing as One’s Facebook Page – be sure to check them out!
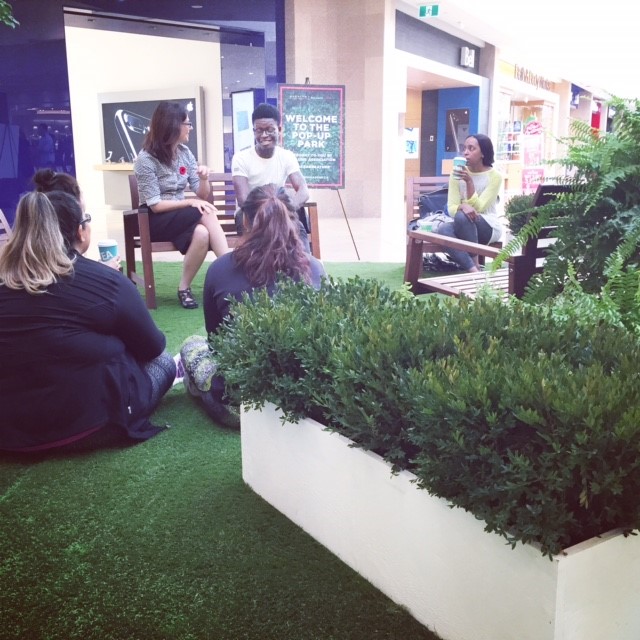

It was such an honour to hear Joseph’s story of overcoming lung cancer and to share what the research community is working on. We all agreed – more money for lung research!
Remember, everything shared with #takeabreather is being curated at breathingasone.ca – take a look and make your contribution today!
Don’t forget, there are three ways that you can get involved:
VISIT THE POP-UP PARK
- Pop in and take a breather and a selfie, and share it on social
media with #takeabreather
- We even have our very own custom #takeabreather Snapchat filter – but you’ll have to visit to see it!
- Location: Sherway Gardens (25 The West Mall)
- When: Thursday, Nov. 3 (11:00-8:00); Friday, Nov. 4 (11:00-8:00); Saturday, Nov. 5 (10:30-8:00); Sunday, Nov. 6 (12:00-5:00)
SHARE #TAKEABREATHER ON SOCIAL MEDIA
- Can’t visit the park? Instead, show us your favourite time and place to take a breather with #takeabreather
- It could be anywhere, anytime – in a field, on a hillside, at dawn or sunset, at the gym, or watching your kids play
- Tell us why you love breathing, why you love this particular breathing moment, what your breath does for you, and any other breathing thoughts you want to share
- Don’t forget #takeabreather
- All contributions will be curated at BreathingasOne.ca
SPREAD THE WORD
- Challenge your friends, family, and extended networks to #takeabreather by forwarding the information above!
It’s time Canadians stop taking our breath for granted. Through Breathing as One and the #TakeABreather campaign, together, we can lead the conversation, and radically change the way we think about breathing.