Supplementary Tables and references
Bluesky Explainer here.
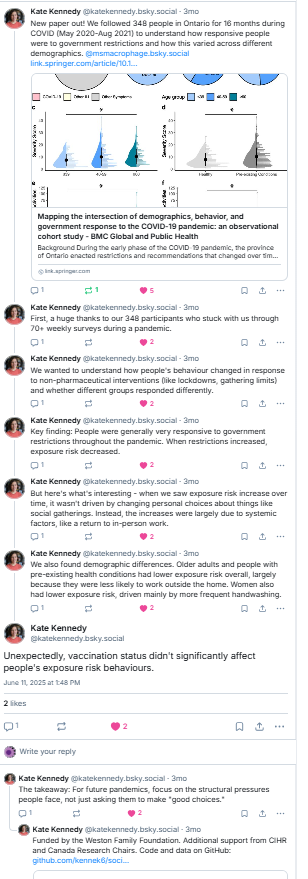
I’m excited to share our review “Rationalizing recommendations for influenza and COVID-19 vaccines”, which we feel makes a strong case for universal influenza and COVID-19 vaccination policies. With almost 500 references & 8 supplementary tables it’s a beast so let me break it down for you….1/n
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264410X25010722#ec0005
We started this >a year ago after conversations with immunologists, policy-makers, and the general public. We felt there were misunderstandings about how well COVID-19 vaccines work. We argue that they work as well or better than influenza vaccines so vaccination policies should be similar. 2/n
Like influenza, everyone but newborns has been exposed to COVID-19 through either vaccination or infection so we only reviewed studies in the post-Omicron/post-vaccine era. There is no doubt that the burden of disease has changed in the Omicron/vaccine era, but does that mean COVID is over? 3/n
Comparable data is hard to find, but when we looked at 2022/23 & 2023/24 data we see that deaths are still higher for COVID than influenza BUT looking at % hides the fact that COVID-19 is more contagious and in 23/24 there were almost 3x as many COVID hospitalizations than influenza. 4/n
There’s a common belief that COVID-19 vaccines don’t provide very good protection against symptomatic infection -is this true? These data are very, very hard to compile because the pace of variant replacement and vaccine changes has been dizzying 5/n
Before we get to the data – I just want to give a huge shoutout to @belongia.bsky.social for leading so many high quality studies on influenza effectiveness – look how easy to compare year-to-year. 6/n
Now look at how complicated it is to compare COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness. In influenza studies it is often possible to assess which strain a person was infected with so you can assess vaccine effectiveness by strain. COVID-19 vaccines are almost never matched with the circulating variants.. 7/n
…but despite that disadvantage, levels of protection from symptomatic infection and severe disease are similar between COVID & influenza vaccines. Note that protection against symptomatic infection is VERY hard to estimate because people who don’t get sick don’t get tested. 8/n
There has been some frustration that COVID-19 vaccines don’t last longer but neither does protection from either infection or vaccination for other viruses. When we compare protection < 3 months and > 3 months, COVID-19 vaccines look pretty good, esp considering rapid variant change 9/n
We also make a case to increase to increase the range of vulnerable populations. Canada has been a leader in including congregate living and equity-deserving groups in priority populations (#elbowsup !) but people living with lung and heart issues should be included 10/n.
Vaccine programs are decided by more than efficacy and efficacy – here’s a summary of what the National Advisory Council on Immunization (Canada) includes. Our review doesn’t address the programmatic, cost, and social considerations, which are also important. 11/n
There are still a lot of unknowns, but we feel strongly that universal & free COVID-19 and influenza vaccines would be a good investment in health, health systems, and attendance at work and school. Thank you to the brilliantly detail oriented Dr.@jabreznik.bsky.social and infl Dr Matt Miller Fin!